In the article “Is Gasless MIG Welding Easier Than Stick?” we will explore the question many welding enthusiasts have pondered: which method is easier, gasless MIG welding or stick welding? While both techniques have their advantages and disadvantages, this article aims to provide a clear comparison of the two, allowing you to make an informed decision based on your specific needs and preferences. So, whether you are a seasoned welder or just starting out, let’s dive into the fascinating world of gasless MIG welding and stick welding to find out which one reigns supreme in terms of ease.
Understanding the Fundamentals of both Welding Processes
What is gasless MIG welding?
Gasless MIG welding, also known as Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW), is a welding process that uses a continuously fed electrode wire to create a weld. Unlike traditional MIG welding, which requires a shielding gas to protect the weld pool from atmospheric contamination, gasless MIG welding uses a flux-cored wire that generates its own shield when it melts. This process is suitable for outdoor welding or in environments where wind or drafts might affect the effectiveness of the shielding gas.
What is stick welding?
Stick welding, also known as Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW), is one of the oldest and most widely used welding processes. It involves using a flux-coated electrode, commonly known as a stick or rod, to create an arc between the electrode and the workpiece. The heat generated by the arc melts the electrode, which then forms the weld joint. The flux coating on the electrode provides shielding gases and creates a slag that protects the weld pool from atmospheric contamination.
Key differences between the two methods
The main difference between gasless MIG welding and stick welding lies in their respective electrode types and shielding methods. Gasless MIG welding uses a flux-cored wire, whereas stick welding uses a flux-coated electrode. Gasless MIG welding generates its own shielding gas through the flux, while stick welding relies on the flux coating on the electrode to provide shielding. Another significant difference is the equipment used – gasless MIG welding requires a MIG welding machine, while stick welding requires a welding power source that can provide direct current (DC) in the form of a welding machine or generator.
Skill Level Required for both Methods
Degree of proficiency required for gasless MIG welding
Gasless MIG welding is generally considered to be more beginner-friendly compared to stick welding. The process offers better control and easier manipulation of the weld pool due to its continuous wire feeding and automatic regulation of the wire speed. The ease of use makes gasless MIG welding an attractive option for those new to welding or those who require a simpler welding process.
Understanding the skill level required for stick welding
Stick welding, on the other hand, typically requires a higher skill level and more practice to master. The welder needs to manually control the electrode position and maintain the correct arc length and angle. The manual manipulation of the electrode can be challenging, especially when welding in difficult positions or on thicker materials. Stick welding often requires a steady hand and precise control to produce high-quality welds.
Contrasting the level of expertise needed for both methods
In terms of skill level, gasless MIG welding is generally considered easier for beginners to learn. The continuous wire feeding and automatic regulation of wire speed make it more forgiving and intuitive. Stick welding, on the other hand, requires a higher level of expertise and mastery of various techniques to produce satisfactory results. While both methods can produce quality welds, gasless MIG welding may be better suited for beginners or those seeking a simpler welding process.
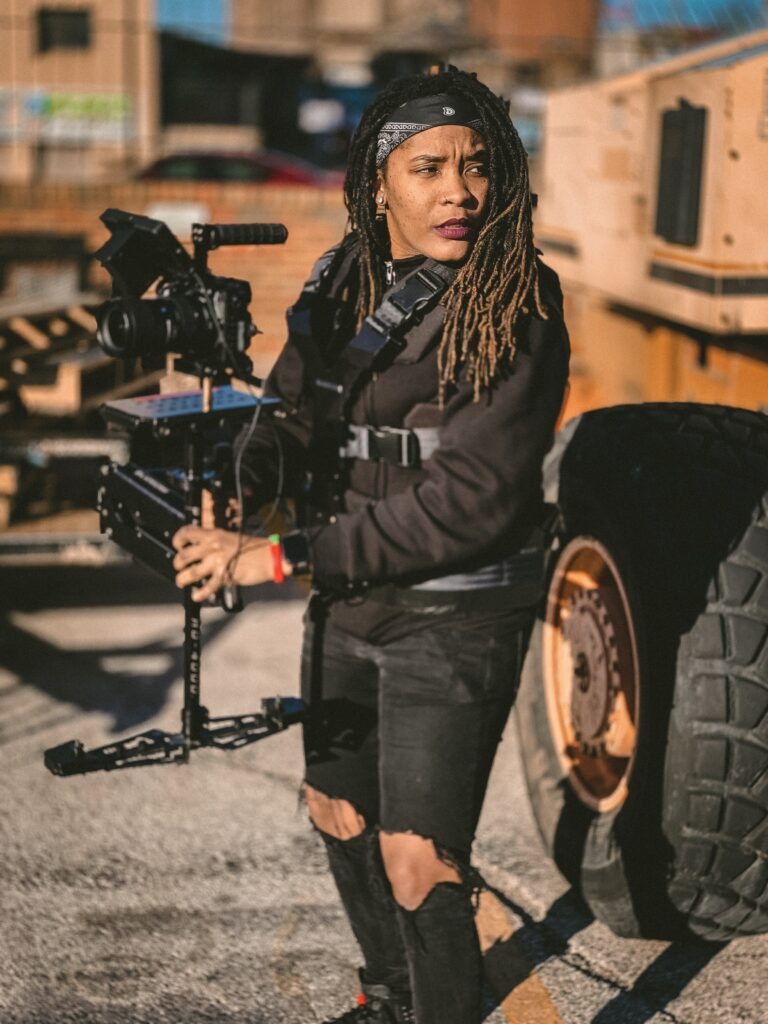

Equipment and Tools Required
Necessary equipment for gasless MIG welding
To perform gasless MIG welding, you will need a gasless MIG welding machine or a MIG welding machine that supports the gasless MIG welding process. Additionally, you will require a suitable flux-cored wire, welding gloves, a welding helmet with a suitable shade level for protection, welding pliers to trim and clean the wire, and appropriate safety gear such as a welding jacket and safety glasses.
The tools needed for stick welding
For stick welding, the essential equipment includes a welding power source that can provide direct current, welding cables and connectors, a welding electrode holder, welding gloves, a welding helmet with a suitable shade level, welding pliers for electrode manipulation, and necessary safety gear such as a welding jacket and safety glasses. Additionally, a chipping hammer or wire brush may be needed to remove slag from the welded joints.
A comparison of the equipment required for both methods
In terms of equipment, gasless MIG welding requires a specialized gasless MIG welding machine and a flux-cored wire. Stick welding, on the other hand, requires a welding power source that provides DC and a suitable stick electrode. While both methods require similar safety gear and basic welding tools, the specialized equipment needed for gasless MIG welding may have cost implications.
The Process of Gasless MIG Welding
Understanding the basic steps in gasless MIG welding
Gasless MIG welding involves several key steps. Firstly, ensure that you have the right safety gear and properly set up your work area. Next, prepare the welding machine by inserting the flux-cored wire and setting the appropriate wire speed and voltage settings according to the material being welded. Once the machine is ready, position the welding gun at the desired starting point, keeping a consistent distance between the gun and the workpiece. Pull the trigger to initiate the wire feed and arc, and then move the gun slowly along the joint, maintaining a steady pace and angle to create a continuous weld.
Procedures involved in advanced gasless MIG welding
Advanced gasless MIG welding techniques involve the use of different wire feed speeds and voltage settings to optimize the weld bead appearance and penetration. Adjusting the wire speed allows for customization of the weld bead size, while adjusting the voltage helps control the heat input and penetration depth. Additionally, advanced gasless MIG welding techniques may involve the use of different wire types and flux compositions to suit specific welding applications and material types.
Safety measures in gasless MIG welding
When performing gasless MIG welding, it is essential to prioritize safety. Make sure to wear appropriate safety gear, including welding gloves, a welding helmet with the correct shade level, a welding jacket, and safety glasses. Ensure that the work area is well-ventilated to prevent the buildup of fumes. Additionally, be cautious of the hot workpiece and the molten metal, as they can cause burns. Finally, always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for operating the gasless MIG welding machine and maintaining safe welding practices.

The Process of Stick Welding
Walking through the steps of stick welding
Stick welding follows a series of steps to create a strong and reliable weld. Start by preparing the work area and ensuring you have the necessary safety gear. Set up the welding machine or generator by connecting the welding cables and electrode holder. Choose the appropriate electrode for the welding task and insert it into the electrode holder. Establish the arc by striking it against the workpiece and maintain the correct arc length. Once the arc is established, move the electrode in a controlled manner along the joint, ensuring proper bead placement and penetration. Finally, remove any slag that forms after each weld pass and continue the process until the desired weld is completed.
Protection steps to take while stick welding
Stick welding involves various safety considerations to protect yourself and others. Wear welding gloves, a welding helmet with the correct shade level, a welding jacket, and safety glasses to shield yourself from sparks, UV radiation, and heat. Ensure that the work area is well-ventilated to minimize the inhalation of welding fumes. Additionally, be cautious of electrical hazards by maintaining proper grounding and avoiding water or damp surfaces. It is crucial to handle the hot electrode holder and the hot workpiece with care to prevent burns.
Exploring advanced techniques in stick welding
Advanced stick welding techniques include adjusting the welding parameters such as amperage and electrode angle to achieve desired results. Controlling the amperage allows for customization of the heat input and penetration depth. Varying the electrode angle also affects the bead appearance and penetration. Additionally, skilled stick welders can manipulate the weaving technique, where the electrode is moved side to side, to create wider welds and improve the overall aesthetics of the weld joint.
Performance Comparison of Gasless MIG and Stick Welding
Quality of weld produced by gasless MIG
Gasless MIG welding can produce high-quality welds when done correctly. The continuous wire feeding and automatic regulation of wire speed allow for better control and consistent weld bead formation. This process also enables deep penetration into the workpiece, resulting in strong and durable welds. However, achieving a smooth and aesthetically pleasing weld bead can be challenging with gasless MIG welding, as the flux-cored wire may create a rougher appearance compared to other welding processes.
Strength of weld produced by stick welding
Stick welding is known for producing robust and structurally sound welds. The manual control and direct heat input make it capable of achieving deep penetration and strong bonding. Stick welding is particularly well-suited for heavy-duty applications that require high strength and reliability. Although achieving visually appealing weld beads may require more skill and practice, the strength of the welds produced by stick welding is often highly regarded.
Comparing the performance of the two welding techniques
When comparing the performance of gasless MIG welding and stick welding, it is essential to consider the specific requirements of the welding application. Gasless MIG welding excels in providing better control and ease of use, making it suitable for beginners or for applications where speed and convenience are important. Stick welding, on the other hand, offers superior strength and is often preferred for heavy-duty applications or situations where aesthetics are less critical. Ultimately, the choice between the two methods depends on the desired outcome and the specific welding requirements.

Cost Implications of both Welding Techniques
Cost of equipment and materials for gasless MIG welding
Gasless MIG welding typically requires specialized equipment, such as a gasless MIG welding machine, which can have a higher upfront cost compared to other welding machines. Additionally, the cost of flux-cored wire, welding gloves, a welding helmet, and other necessary tools should be taken into account. However, gasless MIG welding can be more cost-effective in the long run, as it eliminates the need for purchasing and refilling shielding gas cylinders.
Cost factors in stick welding
Stick welding generally has lower equipment costs compared to gasless MIG welding. A welding power source that provides direct current and a suitable stick electrode are the primary requirements. However, the cost of electrode consumables and other accessories such as welding gloves and a welding helmet should also be considered. Stick welding may also involve the regular purchase of shielded electrodes as they are consumed during the welding process.
Comparing the overall cost of both methods
When comparing the overall cost of gasless MIG welding and stick welding, it is important to weigh the initial equipment costs against the long-term costs. Gasless MIG welding may have a higher upfront investment due to the specialized equipment required. However, the elimination of shielding gas costs can result in long-term savings. Stick welding, on the other hand, has lower initial equipment costs but may require more frequent purchases of electrodes. The overall cost will depend on the frequency of welding and the specific needs of the welding project.
The Versatility of Gasless MIG Vs Stick Welding
Range of materials that can be welded with gasless MIG
Gasless MIG welding is versatile and suitable for welding a wide range of materials. It can be used on mild steel, stainless steel, and even some non-ferrous metals. The process is especially effective for welding thicker materials and is commonly used in automotive, construction, and heavy equipment industries. Its ability to operate in outdoor environments with varying wind conditions makes it a preferred choice for field work.
Understanding the versatility of stick welding
Stick welding is known for its versatility and ability to weld various materials, including carbon steel, stainless steel, cast iron, and certain non-ferrous metals. It can handle a wide range of material thicknesses and is commonly used in construction, maintenance, and fabrication industries. Stick welding can be performed indoors and outdoors, making it a flexible choice for different work environments.
Determining which method is more adaptable
When considering the adaptability of gasless MIG welding versus stick welding, it is crucial to assess the specific requirements of the welding project. Gasless MIG welding offers versatility in terms of material compatibility and the ability to weld in outdoor conditions. Stick welding, on the other hand, provides flexibility in terms of material compatibility and the ability to work in various environments. Both methods have their strengths and can be adapted to a wide range of applications, so the choice depends on the specific needs and constraints of the project.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Gasless MIG Welding
Pros of using the gasless MIG welding technique
Gasless MIG welding offers several advantages. It is relatively easy to learn and is suitable for beginners or those new to welding. The continuous wire feeding and automatic regulation of wire speed provide better control and ease of use. Gasless MIG welding is also ideal for outdoor applications, as it generates its own shielding gas through the flux-cored wire. Additionally, the absence of a shielding gas cylinder reduces the equipment setup and maintenance requirements.
Cons of gasless MIG welding
While gasless MIG welding has its advantages, there are also some disadvantages to consider. The rougher appearance of the weld bead due to flux-cored wire can be a drawback for applications that require aesthetically pleasing welds. The reliance on the flux-cored wire for shielding may also lead to potential porosity or contamination issues if not properly controlled. Additionally, the specialized gasless MIG welding equipment can have a higher upfront cost compared to other welding machines.
Common challenges in gasless MIG welding
Some common challenges in gasless MIG welding include wire feeding issues, improper weld bead formation, and difficulties with controlling the heat input. Ensuring proper wire tension, selecting the correct wire feed speed and voltage, and maintaining a consistent angle and distance during welding can help overcome these challenges. Practice and familiarity with the process can also improve the overall welding experience with gasless MIG welding.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Stick Welding
Benefits of stick welding
Stick welding offers several advantages that make it a popular choice among welders. It can produce strong, reliable, and durable welds, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. Stick welding is versatile and can be used on a wide range of materials and thicknesses. It is also compatible with both indoor and outdoor welding environments. Additionally, stick welding requires minimal equipment setup and can be performed with relatively simple welding machines or generators.
Downsides of the stick welding method
Despite its advantages, stick welding has some disadvantages to consider. It requires a higher skill level and more practice to master compared to other welding processes. The manual control of the electrode position and maintaining the correct arc length and angle can be challenging, especially for beginners. Stick welding may also produce more spatter compared to other welding methods, requiring additional post-weld cleaning.
Common difficulties faced in stick welding
Stick welding presents some common difficulties, such as inconsistent arc starts, electrode sticking, and difficulty in achieving smooth and aesthetically pleasing weld beads. Ensuring proper electrode manipulation, controlling the arc length, and adjusting the welding parameters can help address these challenges. Regular practice and experience are key to improving stick welding skills and overcoming the inherent difficulties.
In conclusion, gasless MIG welding and stick welding are two popular welding processes with their own strengths and weaknesses. Gasless MIG welding offers easier control and manipulation, making it more beginner-friendly and suitable for outdoor applications. Stick welding, on the other hand, produces strong and durable welds but requires a higher skill level. The choice between the two methods depends on factors such as the skill level of the welder, welding requirements, material compatibility, and budget considerations. Ultimately, both processes have their place and can be proficiently used to achieve quality welds.

